Load balancing
Load balancing is a feature designed to distribute available power efficiently among multiple chargers in a charging zone.
It prevents overloading the grid and ensures that all connected vehicles receive optimal power while staying within the set grid limitations.
You can use our dynamic load balancing to distribute power to chargers in real-time while maximizing the site’s charging capacity.
Utilize sequential load balancing to create a virtual queue by prioritizing the users who arrive first, while allocating the remaining power to the next users in line.
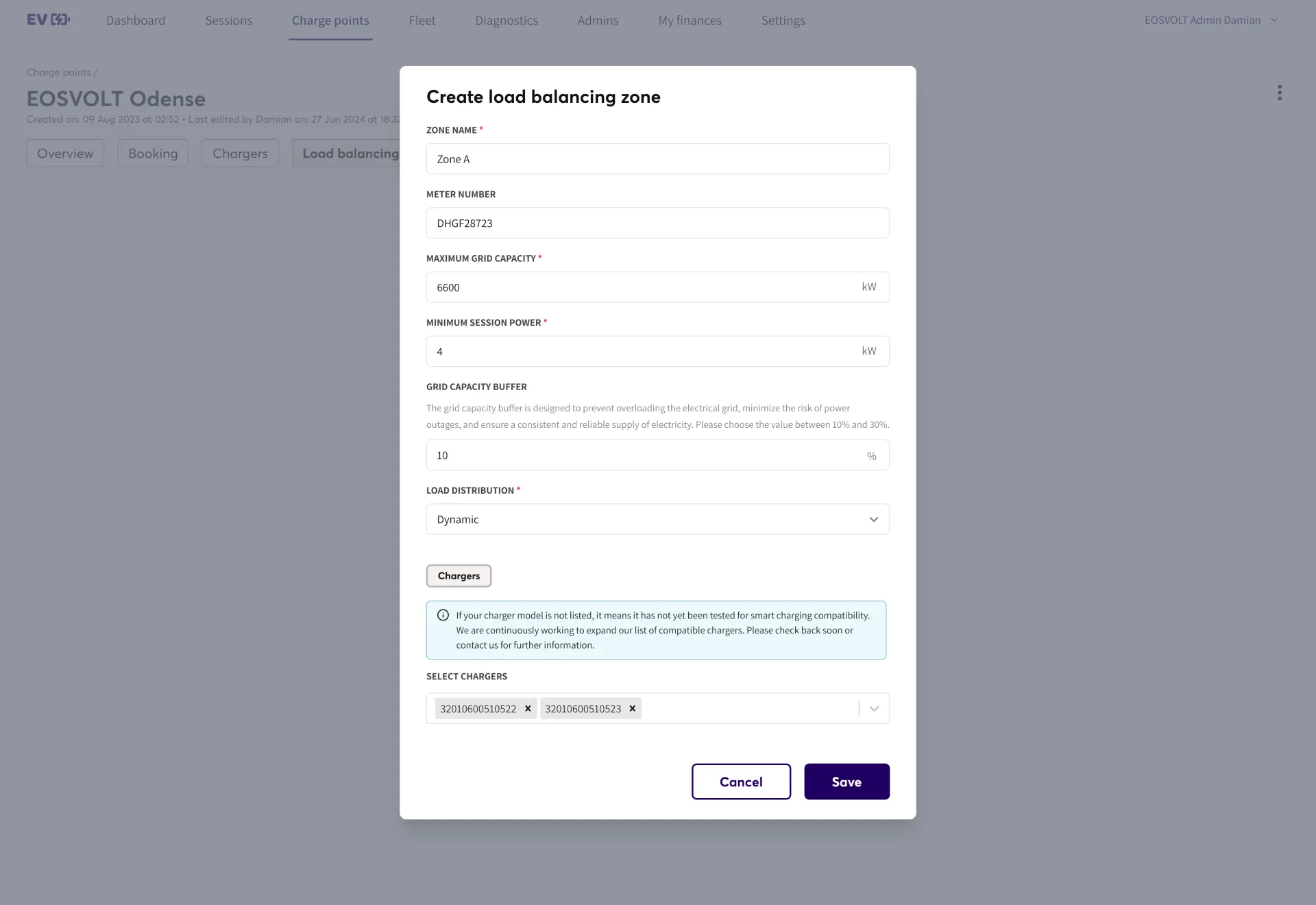
Zone Name
A user-defined name for the load balancing zone. This helps in identifying and managing different charging areas within a site.
Meter Number
The unique identifier assigned to the meter measuring power consumption in the load balancing zone. This number is provided by the electric company.
Maximum Grid Capacity
The total power available for charging within the defined load balancing zone, measured in kilowatts (kW). This value ensures that chargers do not exceed the site's electrical capacity.
Minimum Session Power
The minimum power required per charging session to ensure a stable and effective charging process. This helps in preventing extremely low charging rates that may not be beneficial for users.
Grid Capacity Buffer
A safeguard that reserves a percentage of the total available power to account for fluctuations in the grid and the presence of other electrical appliances. Instead of utilizing the full maximum grid capacity, only a reduced percentage is allocated for charging. For example, if the maximum grid capacity is 3600 kW and a 10% buffer is set, only 3240 kW (90% of 3600 kW) will be available to the chargers. This ensures stability and prevents potential overloads.
Load Distribution
Determines how the available power is distributed among chargers in the zone. Options may include:
- Static: Each charger is assigned a fixed amount of power.
- Dynamic: Power is distributed in real-time based on the number of active charging sessions and their demand.
Chargers
The list of chargers assigned to this load balancing zone. Only compatible chargers can be added. If a charger is not listed, it may not yet be tested for smart charging compatibility.
Select Chargers
Allows users to select specific chargers from the available list to be included in this load balancing zone.
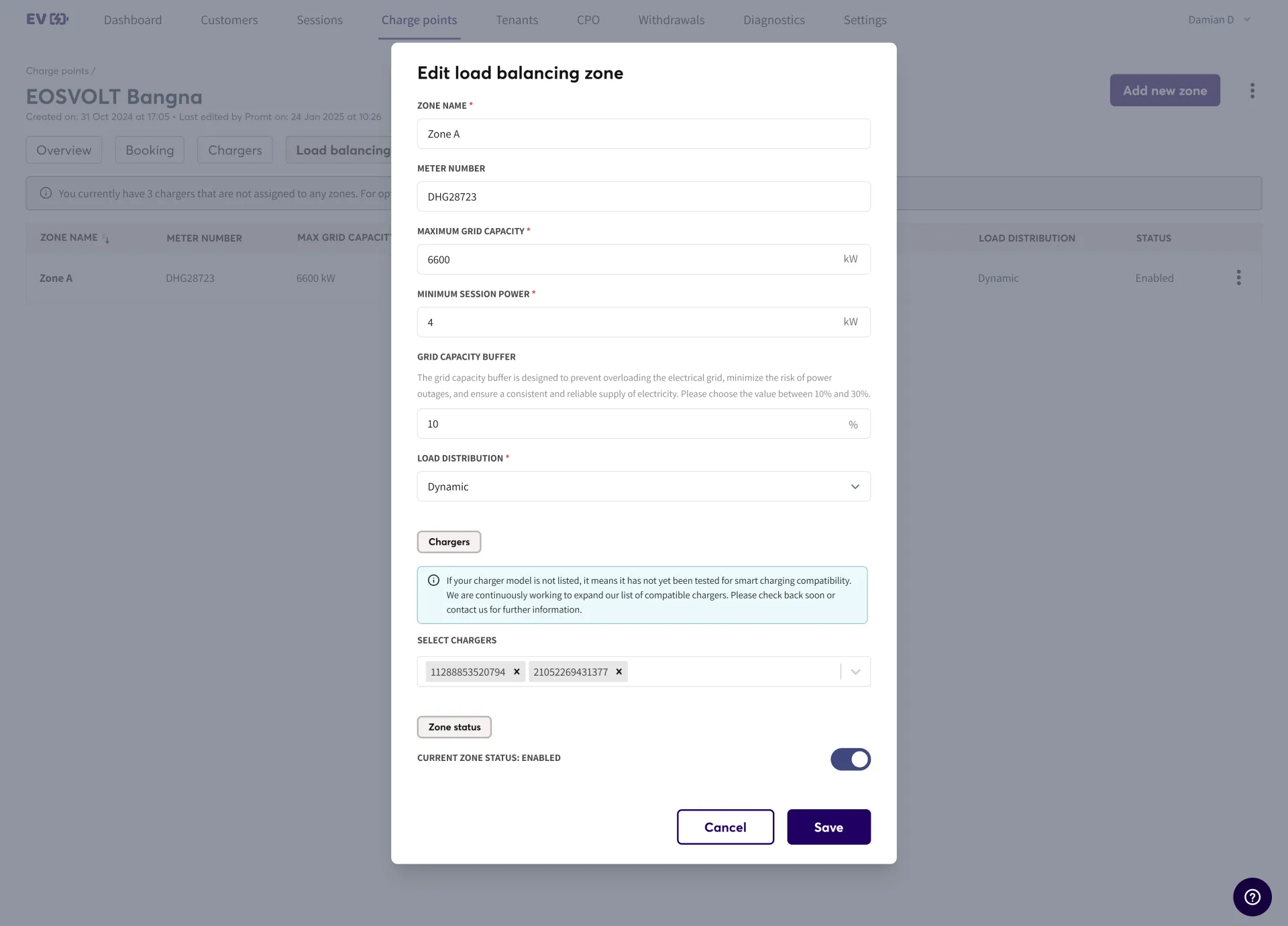
Zone Status Toggle
This toggle becomes available only after a load balancing zone has been created. When enabled, the chargers in this zone will operate under the configured load balancing settings. If disabled, the zone is deactivated, and chargers in that zone will not receive any allocated power from the load balancing system. This feature is useful for maintenance, troubleshooting, or temporarily shutting down a zone without removing its configuration.
- Ensure that the maximum grid capacity reflects the actual power available at the site.
- Set an appropriate grid capacity buffer to prevent power fluctuations from affecting charger performance.
- Use dynamic load distribution if power demand varies frequently among chargers.
- Assign meters correctly to monitor real-time consumption accurately.
- Regularly review and adjust settings based on charging demand and grid stability.
- Sequential Load Balancing in Charging: The load balancer prioritizes which EV charger or charging session to activate first, then moves on to the next, and so on. This approach ensures that the power available from the grid or a local transformer is distributed efficiently across multiple charging stations, preventing overloading and maximizing charging capacity without exceeding supply limits.
- Scenario: Imagine a charging station with 5 EV chargers, but the available grid power can only fully charge 3 cars at once. A sequential load balancer might charge the first 3 cars until their demand reduces, then allocate power to the remaining cars in sequence to ensure all vehicles get charged without tripping the grid.
- Utilize sequential load balancing to create a virtual queue by prioritizing the users who arrive first, while allocating the remaining power to the next users in line.
